Rotary Engine | How It Works, History, Pros & Cons, and More
The rotary engine is a special type of engine that is usually used in some high-performance cars. The traditional piston engine works based on up-and-down motion. In comparison, rotary engines use smooth rotational movement to produce power.
In this article, I will cover what a rotary engine is, how it works, why it’s often called a rotary motor, and why brands like Mazda famously used it in sports cars, along with other important facts. You will also learn about the variants of rotary engines, their real-world applications, and the future of rotary motors and engines.
Quick Overview: Rotary Engine 📄
A rotary engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a triangular rotor instead of pistons. The Wankel rotary engine is the most common type, where the combustion phases, including intake, compression, ignition, and exhaust, occur in different housing areas.
It’s compact, smooth at high RPMs, and used in cars like the Mazda RX-7 and RX-8. Pros include fewer moving parts and high-revving power. Cons include higher fuel consumption, emissions, and specialized maintenance.
Table of contents
- What Is a Rotary Engine?
- Components and Combustion Process of a Rotary (Wankel) Engine
- How a Rotary (Wankel) Engine Works
- Why the Name “Wankel” for Rotary Engine?
- History & Development of Rotary Engines
- Sachs Rotary Engine – A Lesser-Known Variant
- Pros & Cons of Rotary Engines
- Rotary Engine Cars, Applications, and Their Future
- Conclusion
- FAQs
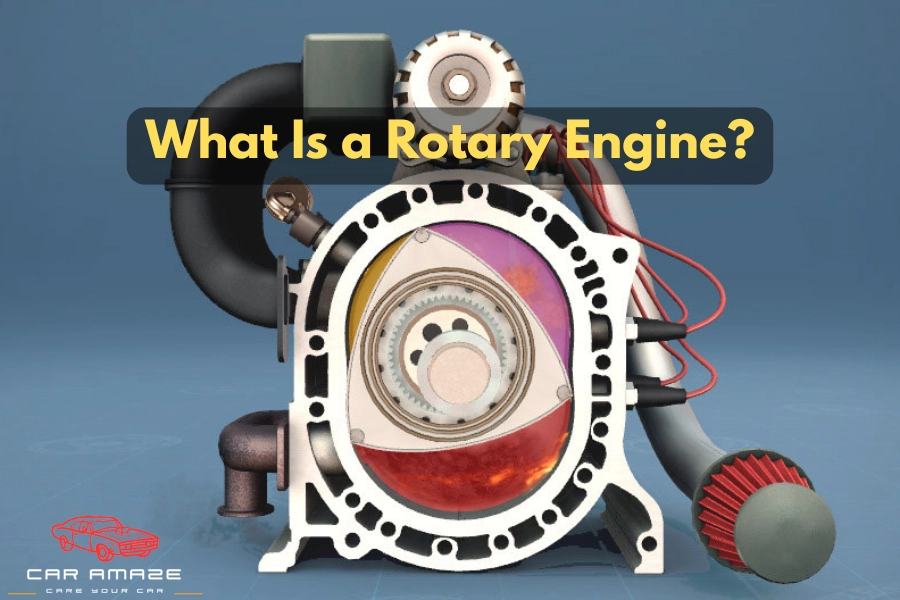
What Is a Rotary Engine?
A rotary engine is a special type of internal combustion engine that works on a triangular rotor instead of pistons. The rotation of the triangular rotor produces the power in the rotary engine. In normal piston engines, the power is produced through the up and down movement of pistons.
The most successful and widely known version of this technology is the Wankel rotary engine. Normally, when people say “rotatory engine,” they are referring to the “Wankel rotary engine.”
Rotary Engine vs. Piston Engine (Quick Comparison)
Rotary engine: Uses a spinning rotor, fewer moving parts, and a compact design. It delivers smooth power at high RPMs and generally produces less vibration than piston engines. Its compact size makes it ideal for sports cars and lightweight vehicles.
Piston engine: Uses pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts with reciprocating motion. It tends to be more fuel-efficient at lower RPMs and is easier to maintain due to widespread familiarity and available parts. Piston engines are also more versatile for a wide range of vehicle sizes and applications.
The word “motor” is commonly used to describe any power-producing machine. Due to this reason, you will often hear the terms “rotary engine” and “rotary motor” used interchangeably.
Components and Combustion Process of a Rotary (Wankel) Engine
The Wankel rotary engine works on the same four combustion phases but in a completely different way.
Core components of a rotary engine
Here are the core components of a rotary engine:
Rotor: A triangular-shaped component that spins inside the housing. It is the main moving part that generates power through its continuous rotation.
Housing: A specially shaped chamber (trochoidal shape) that holds the rotor and helps the engine burn fuel efficiently.
Eccentric shaft: Converts rotor motion into usable rotational power. It acts similarly to a crankshaft in piston engines and delivers engine output to the drivetrain.
The Trochoidal Chamber
The housing is in a trochoidal shape instead of circular. Its trochoidal shape allows the rotor to maintain tight seals while creating separate chambers for combustion. This trochoidal shape is essential for proper rotary engine functions.
The Four Combustion Phases

In a rotary engine, the four phases of combustion occur simultaneously in different areas of the housing. On the contrary, in a piston engine, all combustion phases happen in the piston. The unique design and simultaneous occurrences of all combustion phases in different places in the housing deliver power smoothly.
These are the 4 combustion phases:
- Intake: The rotor draws in the air-fuel mixture into the chamber.
- Compression: The mixture is compressed as the rotor moves, preparing it for ignition.
- Ignition (Power): The compressed mixture is ignited. It produces the actual force that spins the rotor.
- Exhaust: Spent gases are expelled from the chamber.
Each rotor rotation delivers multiple power strokes, which is why rotary engines are known for smooth and high-revving performance.
How a Wankel Rotary Engine Works
The Wankel rotary engine works in the same four combustion phases as a piston engine. The difference is in how these four phases occur in a rotary engine. As you know, the rotary engine consists of 3 main engine components: rotor, housing, and eccentric shaft. The components exist and work in the trichoidal chamber.
The Trochoidal Chamber
The inside of the housing has a special curved shape (called an epitrochoid). As the triangular rotor spins, its corners stay pressed against the housing using apex seals.
This creates three sealed spaces (combustion chambers) between the rotor and the housing. These spaces grow and shrink, allowing the engine to take in air, compress it, burn it, and push exhaust out.
Working of The Four Combustion Phases
Instead of occurring in one cylinder, the four phases happen simultaneously in different areas of the housing. The four combustion phases in a Wankel rotary engine are
- Intake
- Compression
- Ignition (power)
- Exhaust
One rotor creates three power strokes for every full rotor rotation. The eccentric shaft spins three times faster than the rotor. Each rotor rotation delivers multiple power strokes, which is why rotary engines are known for smooth, high-revving performance.
Why Rotary Engines Are Special

Because of this design, rotary engines are known for being:
- Small and lightweight
- Very smooth
- Able to rev very high
Why the Name “Wankel” for Rotary Engine?
The Wankel rotary engine is named after Felix Wankel, the German engineer who invented the design. In 1929, Wankel patented the concept, and in the 1950s, the first working prototypes were developed.
A Wankel engine is a specific type of rotary engine. The name helps distinguish it from other rotary designs that were experimented with but never became widely used.
History & Development of Rotary Engines
1. First Production Cars & Pioneers
The earliest production rotary engine cars came from the German automaker NSU. Models like the NSU Spider and NSU Ro80 showed that the engine ran smoothly. The NSU Spider car has its engine mounted in the back. However, they also showed that the engine had durability problems.
2. Mazda & the Golden Era
No brand is more closely associated with rotary engines than Mazda. The legendary Mazda RX-7 and Mazda RX-8 brought the power of the rotary engine to the global spotlight.

Mazda also made history with the Mazda 787B, the only rotary-powered car to win the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
3. Other Manufacturers and Concepts
Manufacturers such as Mercedes-Benz experimented with rotary engines, including the Mercedes-Benz C111. However, these experiments never led to mass-produced cars.
Sachs Rotary Engine – A Lesser-Known Variant
The Sachs rotary engine is a fascinating but often overlooked variant in rotary history. ZF Sachs developed small Wankel-type rotary engines during the 1960s and 1970s. These engines were designed for compact applications where the engine needs to be small, lightweight, and space-efficient. These were not optimized or made for sports cars.
Common Uses of Sachs Rotary Engines
- Snowmobiles
- Small aircraft
- Industrial equipment
- Lightweight vehicles
The KM48 series, for example, was known for its compact size and smooth operation. Although Sachs rotary engines never became popular, they showed the advantages of rotary engines outside the automobile industry.
Pros & Cons of Rotary Engines
Like other engine types, the rotary engine also has some pros as well as cons.
Advantages of Rotary Engines
The pros of a rotary engine are:
- Compact and lightweight design
- Fewer moving parts than piston engines
- Exceptionally smooth high-RPM operation
- High power-to-weight ratio
Drawbacks of Rotary Engines
Although rotary engines give better performance, they are less popular due to these drawbacks:
- Poor fuel efficiency compared to piston engines
- Higher emissions
- Oil consumption by design
- Apex seal wear and reliability concerns
- Limited availability of skilled mechanics
Due to these drawbacks, this rotatory motor technology in engines has limited adoption.
Rotary Engine Cars, Applications, and Their Future
The most common cars with rotary engines are
- Mazda RX-7
- Mazda RX-8
- Mazda 787B (racing)
Some other applications of the rotatory motor are
- Motorcycles (historical models from Hercules and NSU)
- Small aircraft engines
- Experimental military and industrial power units
Modern Use of Rotary Engine
Nowadays, rotary engines are usually not directly used in cars. They are being reconsidered as range extenders in electric vehicles. These are used in situations where steady engine speed is more important than fuel efficiency at changing speeds.
Future of Rotary Engines
Rotary engines may not dominate modern roads, but they will still be valuable in the future.
Mazda continues to work on integrating the rotary engine with electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles. For example, Mazda is exploring:
- Rotary engines as EV range extenders
- Hydrogen-powered rotary designs
- Advanced materials to reduce wear and emissions
Moreover, rotary motor technology is gaining interest in UAVs, generators, and compact power systems. In short, these are being used in places where size and smoothness are critical.
Conclusion
The rotary engine remains one of the most innovative and unconventional engine designs ever produced. This technology will still have value in the future due to its compact size, smooth performance, and adaptability. However, they are less adopted in road cars due to poor fuel efficiency, apex seal quick wear, and limited skilled mechanics.
FAQs
What is a rotary engine?
A rotary engine is a type of internal combustion engine that produces power through a triangular rotor spinning inside a specially shaped housing. In comparison, the regular engine works through pistons moving up and down.
How does a Wankel rotary engine work?
The Wankel rotary engine uses a triangular rotor that rotates in a trochoidal-shaped housing. The four combustion phases, including intake, compression, ignition, and exhaust, occur in different parts of the housing simultaneously.
What is the difference between a rotary engine and a piston engine?
Rotary engines use a spinning rotor with fewer moving parts, a compact design, and smooth high-rev performance. In contrast, piston engines use reciprocating pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts, and are generally more fuel-efficient and easier to maintain.
What are the main components of a rotary engine?
The core components include the rotor (produces power), housing (trochoidal-shaped chamber), and eccentric shaft (converts rotor motion into usable rotational power). Supporting components include cooling, lubrication, and intake/exhaust systems.
Which cars use rotary engines?
Popular rotary engine cars include the Mazda RX-7, Mazda RX-8, and the Mazda 787B race car. Some lesser-known applications exist in small vehicles, motorcycles, and Sachs rotary engines for tools and snowmobiles.
What are the pros and cons of rotary engines?
Pros: Lightweight, compact, smooth high-rev operation, fewer moving parts.Cons: Poor fuel economy, higher emissions, oil consumption, specialized maintenance, and apex seal wear.




